The surveying industry has undergone a revolution in recent years, thanks to advancements in drone technology. Drones offer a faster, safer, and more cost-effective solution for capturing high-quality geospatial data. But with multiple technologies, platforms, and workflows available, understanding the best approach for your surveying needs can be complex. In this blog, I’ll answer key FAQs about drone surveying, explore the best drones in the industry, and highlight how they are used in the surveying and construction industry.
Photogrammetry vs. LiDAR: Which is Better for Surveying?
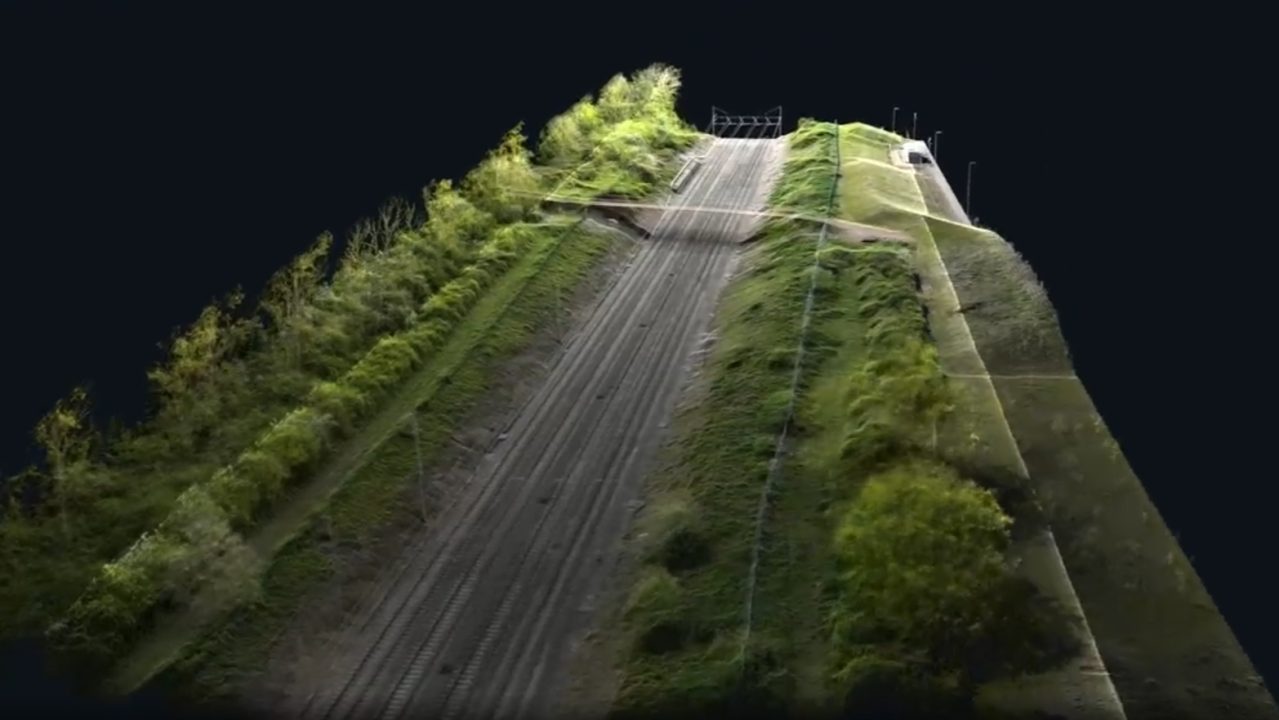
One of the most common questions in drone surveying is whether photogrammetry or LiDAR is the superior choice. The answer is neither and both as it wholly depends on the project requirements:
- Photogrammetry: This technique involves capturing overlapping aerial images and processing them to create 2D and 3D models. It is ideal for large-scale topographical mapping, construction site monitoring, measured building surveys and volumetric calculations. It works best in open environments with clear visibility.
- LiDAR: LiDAR sensors emit laser pulses to measure distances and generate highly accurate 3D point clouds. This method excels in penetrating vegetation and capturing ground-level details, making it perfect for forestry, mining, and infrastructure projects.
Both technologies have their place in surveying, and choosing between them depends on factors like terrain, required accuracy, and project constraints.
How Accurate Are Drone Surveys?
Drone surveys can achieve centimetre-level accuracy with the right equipment and methodology. The level of accuracy depends on factors such as:
- The drone’s positioning system (e.g., RTK or PPK GNSS technology)
- The quality of the camera or LiDAR sensor used
- Ground control points (GCPs) and post-processing techniques
With drones like the DJI Matrice 350 RTK, surveyors can achieve absolute accuracy of up to 1-3 cm, making them a reliable alternative to traditional surveying methods.
The Process of Data Collection and Processing
A standard drone surveying workflow includes the following steps:
Analysis and Integration – The processed data is integrated into CAD, GIS, or BIM workflows for analysis and decision-making.
Planning the Flight – Using software to define flight paths, altitude, and overlap settings in softwares such as DJI Pilot 2 or Flight Hub 2.
Data Capture – The drone autonomously follows the flight plan, collecting imagery or LiDAR data.
Data Processing – Images are processed with photogrammetry software (e.g., Pix4D, DJI Terra) to generate orthomosaics, DEMs, and 3D models. LiDAR data is cleaned and classified using specialised software, or for L2 data in DJI Terra.
Best Drones for Surveying
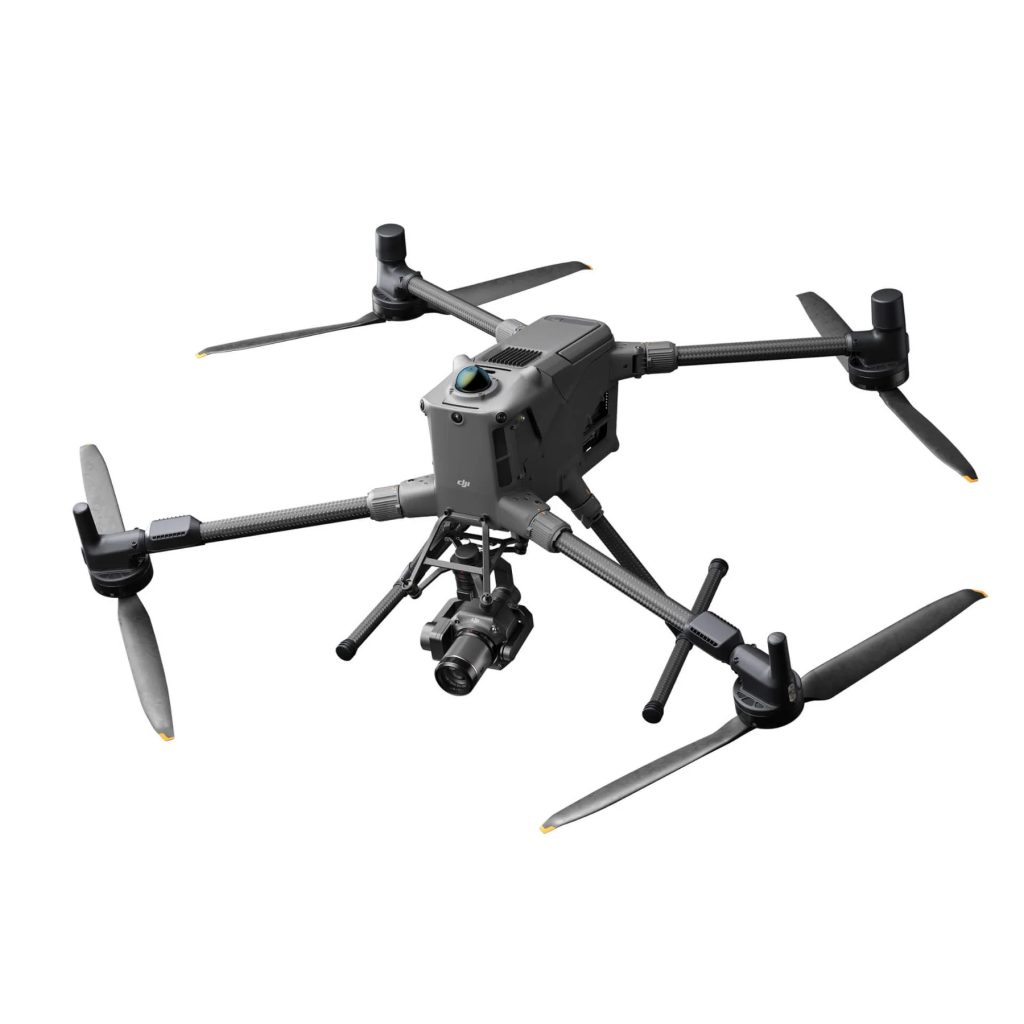
1. DJI Matrice 350 RTK with Zenmuse P1 & L2 Payloads
- The Zenmuse P1 (photogrammetry) features a full-frame 45MP sensor, ideal for large-scale topographic surveys.
- The Zenmuse L2 (LiDAR) delivers high-accuracy point clouds, making it suitable for terrain mapping, forestry, and infrastructure projects.
- With RTK technology, it provides centimetre-level accuracy for demanding surveying tasks.
2. DJI Matrice 4 Enterprise
- The best entry-level photogrammetry drone.
- Full frame 20MP camera with mechanical shutter, perfect for survey grade quality.
- Features advanced obstacle avoidance and AI-powered automation for efficiency.
3. Flyability Elios 3
- A collision-tolerant confined space drone equipped with LiDAR.
- Best for confined space inspections such as tunnels, bridges, and industrial facilities.
- Enhances safety by allowing inspections without the need for scaffolding or human entry.
4. Emesent Hovermap STX
Generates real-time SLAM-based point clouds, even in GPS-denied environments.
A mobile LiDAR mapping solution that can be mounted on drones, vehicles, a backpack or handheld.
Ideal for underground mining, hazardous environments, and detailed infrastructure mapping.
Key Use Cases for Drone Surveying and Construction
Drones are transforming how surveying and construction professionals collect and analyse data. Some of the most common use cases include:
Mining and Quarrying – Improve operational efficiency and safety in open-pit and underground mining projects.
Topographic Surveys – Mass data collection in a short space of time for land development and infrastructure projects.
Volumetric Analysis – Monitor stockpiles, excavation progress, and earthworks with precise volume calculations.
Construction Site Monitoring – Track project progress, identify deviations, and enhance collaboration with real-time data.
Structural Inspections – Conduct safe and efficient inspections of bridges, towers, and industrial structures.
Forestry and Environmental Monitoring – Map vegetation, assess environmental impact, and track land-use changes.
Conclusion
Drone technology is redefining the surveying and construction industries, offering unmatched efficiency, accuracy, and safety. Whether you choose photogrammetry or LiDAR, the right drone and workflow can significantly enhance your data collection capabilities.
For organizations looking to implement drone surveying, investing in top-tier solutions like the DJI Matrice 350 RTK, DJI Matrice 4 Enterprise, Flyability Elios 3, or Emesent Hovermap STX ensures high-quality results for a range of applications.
Are you ready to take your surveying capabilities to the next level? Contact Coptrz today to explore the best drone solutions tailored to your needs!
Follow Coptrz for more insights on drone technology in surveying and beyond!
Download our FREE GVC Training Guide
Learn everything you need to know about becoming a drone pilot with our GVC training guide.
- Get a full course roadmap to understand every step of the journey
- Contains clear answers to all of the frequently asked questions
- Get a transparent and comprehensive breakdown of course costs